How to add and delete blank rows in excel (mac) - Duration: 2:17. Jordan Woodhouse 24,061 views. How to create a table in Microsoft Word 2010 for Mac - Duration: 7:09. Choose Table→Draw Table from the menu bar. Alternatively, click the Draw button in the Draw Borders group of the Ribbon's Tables tab. Drag the mouse diagonally to create a dotted box shape and then let go of the mouse button. Continue drawing row and column dividers.
Home > Articles > Operating Systems, Server > MAC OS X/Other
␡- Building a Table

This chapter is from the book
This chapter is from the book
Topics include the following:
- Inserting a table into a Word document
- Working with table rows and columns
- Adding and populating document headers and footers
- Choosing a page orientation and paper size
- Setting the page margins
- Adding footnotes and endnotes
In the previous chapter, you dealt with Word at the 'tree' level of words, sentences, and paragraphs. But getting more out of Word also requires that you deal with the program at the 'forest' level of pages and documents. This means you need to get familiar with Word's page layout tools.
Page layout refers to how text and paragraphs are laid out on each page, and it involves building tables, adding headers and footers, setting margin sizes, specifying the page orientation, choosing the paper size, and so on. This chapter shows you how to work with these and other page layout features.
Building a Table
Most Word documents consist of text in the form of sentences and paragraphs. However, including lists of items in a document is common, particularly where each item in the list includes two or more details (which means a standard bulleted list won't do the job). For a short list with just a few details, the quickest way to add the list to a document is to type each item on its own line and press Tab between each detail. You could then add tab stops to the ruler (see Chapter 4, 'Working with Text in Word') to line up the subitems into columns.
That works for simple items, but to construct a more complex list in Word, you can build a table, a rectangular structure with the following characteristics:
- Each item in the list gets its own horizontal rectangle called a row.
- Each set of details in the list gets its own vertical rectangle called a column.
- The rectangle formed by the intersection of a row and a column is called a cell, and you use the table cells to hold the data.
In other words, a Word table is similar to an Excel worksheet or an Access datasheet.
Insert a Table
Although Word gives you no less than one-half dozen ways to build a table, you need to know only the most straightforward method.
- Position the insertion point where you want the table to appear.
- Click the Insert tab.
- Click Table.
Click Insert Table to display the Insert Table dialog.
- Specify the number of columns you want in your table.
- Specify the number of rows you want in the table.
Click OK. Word inserts the table.
- Position the insertion point inside a cell and then add the text that you want to store in the cell. Repeat for the other cells in the table.
- Click the Layout tab.
Use the Table Column Width box to set the width of the column.
Select Table Elements
Before you can change the layout or formatting of a table, you need to select the part of the table you want to work with. Here are the techniques to use (note that, in each case, 'Layout' refers to the table's Layout tab, which appears to the right of the Table Design tab):
- Select a cell—Select the cell and then click Layout, Select, Select Cell (or triple-click anywhere in the cell).
- Select two or more adjacent cells—Select the top-left cell you want to include in the selection, then drag the mouse down and to the right to include the other cells.
- Select a row—Click any cell in the row and then click Layout, Select, Select Row.
- Select two or more adjacent rows—Select at least one cell in each row and then click Layout, Select, Select Row.
- Select a column—Click any cell in the column and then click Layout, Select, Select Column.
- Select two or more adjacent columns—Select at least one cell in each column and then click Layout, Select, Select Column.
- Select the entire table—Click any cell in the table and then click Layout, Select, Select Table.
Format a Table
To change the formatting of the table cells, you select the cells you want to work with and then use Word's standard formatting tools (font, paragraph, and so on). For more table-specific formatting, you can use the Table Design tab.
- Click inside the table.
- Click the Table Design tab.
Click the More button of the Table Styles gallery.
Click the style you want to apply to the table.
- Click Header Row to toggle header formatting on and off for the first row. For example, in some styles the first row is given darker shading, top and bottom borders, and a bold font.
- Click Total Row to toggle total formatting on and off for the bottom row.
- Click Banded Rows to toggle alternating formatting for all the rows.
- Click First Column to toggle special formatting on and off for the first column.
- Click Last Column to toggle special formatting on and off for the last column.
Click Banded Columns to toggle alternating formatting for all the columns.
- Select the cells you want to format and then use the Shading gallery to click a background color.
Select the cells you want to format and then use the Border Styles gallery to click a border style.
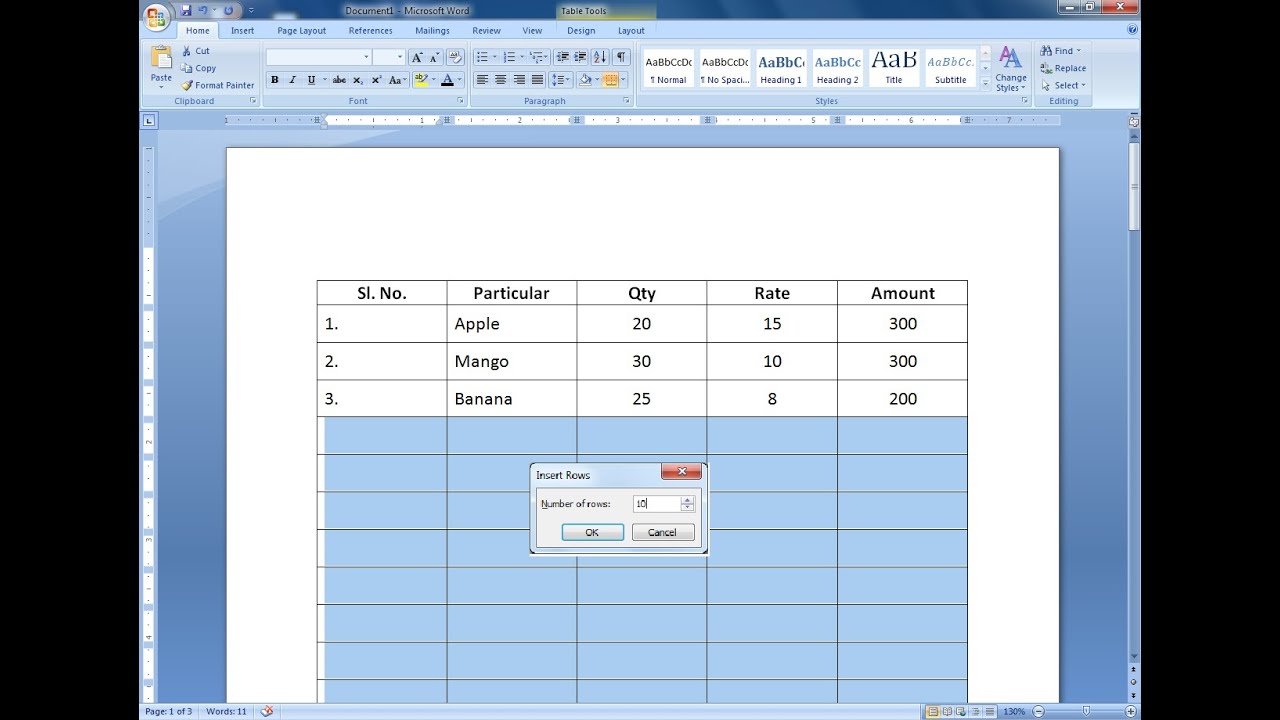
Insert New Rows
There are times when you need to add more data to a table. Word provides several tools that enable you to expand a table. If you're adding new items to the table, you need to add more rows.
How Do I Add A Row To A Table In Word For Macro
To add a new row at the end of the table, position the insertion point in the lower-right cell—that is, the last column of the last row—and press Tab.
- Click the Layout tab.
- To add a new row above an existing row, position the insertion point inside the existing row and then click Insert Above.
To add a new row below an existing row, position the insertion point inside the existing row and then click Insert Below.
Insert New Columns
If you need to add more details to each item in your table, you need to add more columns.
- Click inside an existing column.
- Click the Layout tab.
- To add a new column to the left of an existing column, click Insert Left.
To add a new column to the right of an existing column, click Insert Right.
Delete Table Elements
If you no longer need a part of your table—for example, a cell, a row, or a column—you can delete it. You can delete multiple cells, rows, or columns, and, if necessary, you can delete the entire table.
Select the table element you want to delete.
- Click the Layout tab.
- Click Delete.
Click the command that represents the type of table element you want to delete. If you click the Delete Cells command, the Delete Cells dialog opens.
- Click whether you want to shift the remaining cells to the left or up, or if you would rather delete the entire row or column.
Click OK.
Related Resources
- Online Video $239.99
- Online Video $239.99
- Online Video $239.99
On this page:
- Column headings
Overview
In Microsoft Word, it is important to make sure all tables are accessible to those using screen readers. This helps those using screen readers to make sense of the data contained in a table. You should only use a table when it's necessary to convey relationships between pieces of data, and not for layout purposes. When using tables in a Word document, keep them as simple as possible. If necessary, split complex tables into multiple smaller tables. Be sure to designate a header row and use column headings to help describe the data in the table, as well as repeat the column headings on each page the table appears on. You should also ensure the table has alternative text, to describe the contents of the table for those using screen readers.
Designate a header row
There are multiple parts to the process of making a table accessible. The first involves making sure the table has a header row designated. The 'Table Style Options' section of the ribbon on the Table Tools contextual tab lets you indicate that your data has a header row.
To add a table with a header row to a Word document:
- On the ribbon, click Insert, and then click Table.
- Choose how many rows and columns you want for your table.
- On the ribbon, in the 'Table Tools' group, click Design.
- In the 'Table Style Options' group, make sure Header Row is checked.
Column headings
Column headings help describe the content in a table, and should be present to help users understand the content.
To add column headings to a table in Word:
- Place your cursor in the first cell of the top row of the table.
- Type the name for the first column, and press Tab to move to the next column.
- Repeat step 2 for the remaining columns.
Repeat column headings
Column headings should be repeated at the top of a table if the table spans multiple pages.
How Do I Add A Row To A Table In Word For Mac Os
To repeat the column headings:
- Right-click the table, and then click Table Properties.
- In the 'Table Properties' dialog box, click the Row tab.
- In the 'Options' group, make sure Repeat as header row at the top of each page is checked.
- Uncheck the box next to Allow row to break across pages.
- Click OK to accept the changes.
Alternative text
To add alternative text for tables, use the Alt Text tab of the 'Table Properties' dialog box:

This chapter is from the book
This chapter is from the book
Topics include the following:
- Inserting a table into a Word document
- Working with table rows and columns
- Adding and populating document headers and footers
- Choosing a page orientation and paper size
- Setting the page margins
- Adding footnotes and endnotes
In the previous chapter, you dealt with Word at the 'tree' level of words, sentences, and paragraphs. But getting more out of Word also requires that you deal with the program at the 'forest' level of pages and documents. This means you need to get familiar with Word's page layout tools.
Page layout refers to how text and paragraphs are laid out on each page, and it involves building tables, adding headers and footers, setting margin sizes, specifying the page orientation, choosing the paper size, and so on. This chapter shows you how to work with these and other page layout features.
Building a Table
Most Word documents consist of text in the form of sentences and paragraphs. However, including lists of items in a document is common, particularly where each item in the list includes two or more details (which means a standard bulleted list won't do the job). For a short list with just a few details, the quickest way to add the list to a document is to type each item on its own line and press Tab between each detail. You could then add tab stops to the ruler (see Chapter 4, 'Working with Text in Word') to line up the subitems into columns.
That works for simple items, but to construct a more complex list in Word, you can build a table, a rectangular structure with the following characteristics:
- Each item in the list gets its own horizontal rectangle called a row.
- Each set of details in the list gets its own vertical rectangle called a column.
- The rectangle formed by the intersection of a row and a column is called a cell, and you use the table cells to hold the data.
In other words, a Word table is similar to an Excel worksheet or an Access datasheet.
Insert a Table
Although Word gives you no less than one-half dozen ways to build a table, you need to know only the most straightforward method.
- Position the insertion point where you want the table to appear.
- Click the Insert tab.
- Click Table.
Click Insert Table to display the Insert Table dialog.
- Specify the number of columns you want in your table.
- Specify the number of rows you want in the table.
Click OK. Word inserts the table.
- Position the insertion point inside a cell and then add the text that you want to store in the cell. Repeat for the other cells in the table.
- Click the Layout tab.
Use the Table Column Width box to set the width of the column.
Select Table Elements
Before you can change the layout or formatting of a table, you need to select the part of the table you want to work with. Here are the techniques to use (note that, in each case, 'Layout' refers to the table's Layout tab, which appears to the right of the Table Design tab):
- Select a cell—Select the cell and then click Layout, Select, Select Cell (or triple-click anywhere in the cell).
- Select two or more adjacent cells—Select the top-left cell you want to include in the selection, then drag the mouse down and to the right to include the other cells.
- Select a row—Click any cell in the row and then click Layout, Select, Select Row.
- Select two or more adjacent rows—Select at least one cell in each row and then click Layout, Select, Select Row.
- Select a column—Click any cell in the column and then click Layout, Select, Select Column.
- Select two or more adjacent columns—Select at least one cell in each column and then click Layout, Select, Select Column.
- Select the entire table—Click any cell in the table and then click Layout, Select, Select Table.
Format a Table
To change the formatting of the table cells, you select the cells you want to work with and then use Word's standard formatting tools (font, paragraph, and so on). For more table-specific formatting, you can use the Table Design tab.
- Click inside the table.
- Click the Table Design tab.
Click the More button of the Table Styles gallery.
Click the style you want to apply to the table.
- Click Header Row to toggle header formatting on and off for the first row. For example, in some styles the first row is given darker shading, top and bottom borders, and a bold font.
- Click Total Row to toggle total formatting on and off for the bottom row.
- Click Banded Rows to toggle alternating formatting for all the rows.
- Click First Column to toggle special formatting on and off for the first column.
- Click Last Column to toggle special formatting on and off for the last column.
Click Banded Columns to toggle alternating formatting for all the columns.
- Select the cells you want to format and then use the Shading gallery to click a background color.
Select the cells you want to format and then use the Border Styles gallery to click a border style.
Insert New Rows
There are times when you need to add more data to a table. Word provides several tools that enable you to expand a table. If you're adding new items to the table, you need to add more rows.
How Do I Add A Row To A Table In Word For Macro
To add a new row at the end of the table, position the insertion point in the lower-right cell—that is, the last column of the last row—and press Tab.
- Click the Layout tab.
- To add a new row above an existing row, position the insertion point inside the existing row and then click Insert Above.
To add a new row below an existing row, position the insertion point inside the existing row and then click Insert Below.
Insert New Columns
If you need to add more details to each item in your table, you need to add more columns.
- Click inside an existing column.
- Click the Layout tab.
- To add a new column to the left of an existing column, click Insert Left.
To add a new column to the right of an existing column, click Insert Right.
Delete Table Elements
If you no longer need a part of your table—for example, a cell, a row, or a column—you can delete it. You can delete multiple cells, rows, or columns, and, if necessary, you can delete the entire table.
Select the table element you want to delete.
- Click the Layout tab.
- Click Delete.
Click the command that represents the type of table element you want to delete. If you click the Delete Cells command, the Delete Cells dialog opens.
- Click whether you want to shift the remaining cells to the left or up, or if you would rather delete the entire row or column.
Click OK.
Related Resources
- Online Video $239.99
- Online Video $239.99
- Online Video $239.99
On this page:
- Column headings
Overview
In Microsoft Word, it is important to make sure all tables are accessible to those using screen readers. This helps those using screen readers to make sense of the data contained in a table. You should only use a table when it's necessary to convey relationships between pieces of data, and not for layout purposes. When using tables in a Word document, keep them as simple as possible. If necessary, split complex tables into multiple smaller tables. Be sure to designate a header row and use column headings to help describe the data in the table, as well as repeat the column headings on each page the table appears on. You should also ensure the table has alternative text, to describe the contents of the table for those using screen readers.
Designate a header row
There are multiple parts to the process of making a table accessible. The first involves making sure the table has a header row designated. The 'Table Style Options' section of the ribbon on the Table Tools contextual tab lets you indicate that your data has a header row.
To add a table with a header row to a Word document:
- On the ribbon, click Insert, and then click Table.
- Choose how many rows and columns you want for your table.
- On the ribbon, in the 'Table Tools' group, click Design.
- In the 'Table Style Options' group, make sure Header Row is checked.
Column headings
Column headings help describe the content in a table, and should be present to help users understand the content.
To add column headings to a table in Word:
- Place your cursor in the first cell of the top row of the table.
- Type the name for the first column, and press Tab to move to the next column.
- Repeat step 2 for the remaining columns.
Repeat column headings
Column headings should be repeated at the top of a table if the table spans multiple pages.
How Do I Add A Row To A Table In Word For Mac Os
To repeat the column headings:
- Right-click the table, and then click Table Properties.
- In the 'Table Properties' dialog box, click the Row tab.
- In the 'Options' group, make sure Repeat as header row at the top of each page is checked.
- Uncheck the box next to Allow row to break across pages.
- Click OK to accept the changes.
Alternative text
To add alternative text for tables, use the Alt Text tab of the 'Table Properties' dialog box:
- Right-click the table, and then click Table Properties.
- In the 'Table Properties' dialog box, click the Alt Text tab.
- Fill in the description for the table and, if necessary, add a title for the table.
- Click OK to accept the changes.
Prior versions of Word
For instructions for creating an accessible table in Word 2013, see the section on tables in WebAim's Microsoft Word 2013 accessible documents guide.
